Our Services
Our laboratory servics have been segmented into dif frent core functions. Through many tests and test combinations overlap with each other, all sections work in tandem. The segmentation is critical since the techniques, automation and quality process that each section demands is. unique from each other, We of fer a broad range of around 3,000 Clinical laboratory testes and 200 profiles. These profiles comprise of variety of test combinations which are specific to a disease or disorder as well as wellness profiles that are used for health and fitness screening.
 BIOCHEMISTRY
BIOCHEMISTRY
Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. It combines principles of biology and chemistry to understand the molecular mechanisms that underlie various biological functions, such as:
Biochemistry is foundational to many fields, including medicine, pharmacology, biotechnology, and nutrition, as it helps to understand diseases, develop therapies, and improve human health.
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Molecular Biology is a branch of biology that focuses on the molecular basis of biological processes within living organisms. It involves the study of the structure, function, and interactions of molecules essential to life, such as DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Key Areas of Molecular Biology:
Molecular biology often overlaps with biochemistry and genetics and plays a crucial role in fields such as genetic engineering, biotechnology, and medicine, helping to understand diseases at a molecular level and develop targeted therapies.
 CYTOPATHOLOGY
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Cytopathology is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases at the cellular level. It involves examining individual cells or small groups of cells extracted from tissues or bodily fluids to detect abnormalities, including infections, inflammation, and cancer.
Key Features of Cytopathology:
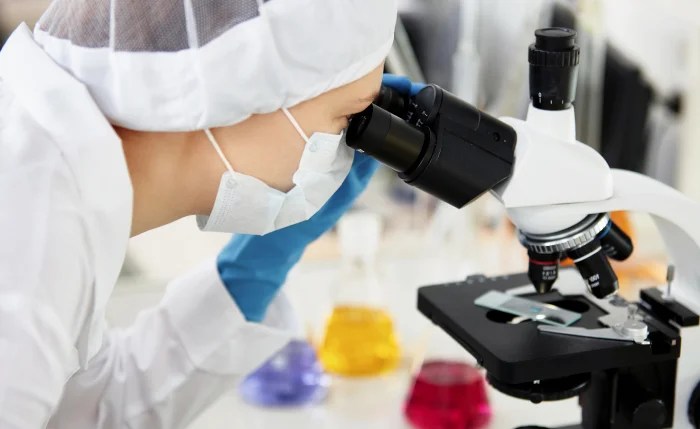 CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
Clinical Pathology is a branch of pathology that focuses on the diagnosis of diseases by analyzing laboratory results derived from bodily fluids (such as blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid), tissues, and cells. It combines laboratory science with clinical medicine to provide essential insights for patient care.
Key Areas of Clinical Pathology:
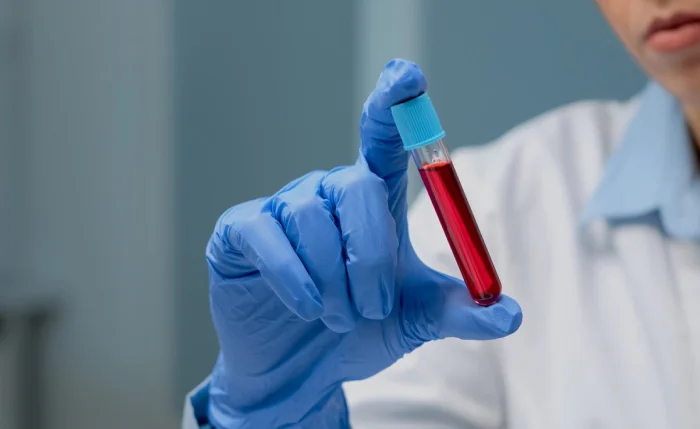 HEMATOLOGY
HEMATOLOGY
Histopathology is the branch of pathology that involves the study of tissue samples under a microscope to diagnose diseases. It examines the structural changes in tissues caused by disease, including alterations in cell morphology, tissue architecture, and the presence of abnormal cells. Histopathology plays a crucial role in identifying the nature of diseases, particularly cancer, infections, and inflammatory conditions.
Key Areas of Histopathology:
Histopathology is essential in providing definitive diagnoses and informing the treatment plans of patients, particularly in oncology, infectious diseases, and chronic conditions.
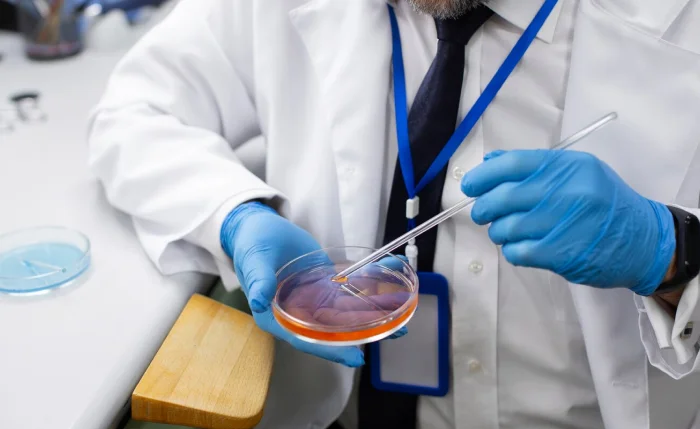 HISTOPATHOLOGY
HISTOPATHOLOGY
Histopathology is the branch of pathology that involves the study of tissue samples under a microscope to diagnose diseases. It examines the structural changes in tissues caused by disease, including alterations in cell morphology, tissue architecture, and the presence of abnormal cells. Histopathology plays a crucial role in identifying the nature of diseases, particularly cancer, infections, and inflammatory conditions.
Key Areas of Histopathology:
Histopathology is essential in providing definitive diagnoses and informing the treatment plans of patients, particularly in oncology, infectious diseases, and chronic conditions.
 TOXICOLOGY
TOXICOLOGY
Toxicology is the branch of science that studies the adverse effects of chemicals, substances, and environmental agents on living organisms, including humans, animals, and ecosystems. It examines the nature, mechanisms, and extent of harmful effects caused by toxins, poisons, and drugs, as well as how these substances can be detected, managed, and prevented.
Key Areas of Toxicology:
Toxicology is essential in various fields, including medicine, pharmacology, environmental science, and regulatory science, ensuring the safety of substances and protecting public health and the environment.
 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a laboratory technique used to detect specific proteins or antigens in tissue sections by using antibodies that bind to these targets. It combines the principles of immunology and histology to identify and localize the presence of specific molecules within tissue samples, often to help diagnose diseases such as cancers, infections, and autoimmune disorders.
Key Aspects of Immunohistochemistry:
 Microbiology
Microbiology
Microbiology is the branch of science that studies microorganisms, which are microscopic organisms too small to be seen with the naked eye. These include bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae. Microbiology focuses on the structure, function, classification, and interactions of these microorganisms with humans, animals, plants, and the environment.
Key Areas of Microbiology:
 Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is a branch of genetics that studies the structure, function, and behavior of chromosomes in cells, especially during cell division. It focuses on understanding chromosomal abnormalities, their implications for human health, and their role in heredity, development, and diseases.
Key Areas of Cytogenetics:
Fair Diagnostic embraces cutting-edge technology to deliver precise and quality results. With advanced LIS, we ensure one of the fastest turnaround times. Experience innovation with Us!
